New Windows 11 Configure Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon Authentication using Group Policy and other methods for Kerberos protocol. Microsoft introduced this group policy in the Windows Insider version.
The new group policy and ADMX settings to configure Hash algorithms for certificate logon introduce agility to PKINIT in the Kerberos protocol. This new policy allows admins to configure hash algorithms for PKINIT (Public Key Cryptography for Initial Authentication) in Kerberos Protocol.
As per the group policy UI, the Configure Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon group policy supports Windows 11 22H1 onwards! I never heard about the Windows 11 22H1 version. This could be an insider version of Windows 11.
Microsoft started using SHA-2 more widely used and recommended SHA-2 instead of SHA-1. There are four states for each algorithm, and there are four algorithms supported by Kerberos authentication. The Secured HASH algorithms are based on the output. The SHA-512 algorithm is based on 512-bit output.
- Disable Enable TLS 1.0 And 1.1 For Internet Explorer EdgeHTML
- Windows 11 New LSA Local Security Authority Policies
4 SHA Algorithms
The following are the 4 supported SHA algorithm options available Configure Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon group policy. I don’t think many organizations are using SHA-128 (SHA1) algorithms anymore. SHA is a Secured HASH Algorithm.
- SHA-1 = Output is 128 bit
- SHA-256 = Output is 256 bit
- SHA-384 = Output is 384 bit
- SHA-512 = Output is 512 bit

New Windows 11 Configure Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon Authentication
There is a new New Windows 11 Configure Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon Authentication policy available in the latest versions of the Windows insider DEV channel.
If the certificate authentication policy is in the “disable” or “do not configure” state, then each algorithm will assume the “Default” state. The SHA algorithm details are explained in the below section of the post.
Group Policy Path -> Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System > Kerberos > Configure Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon.
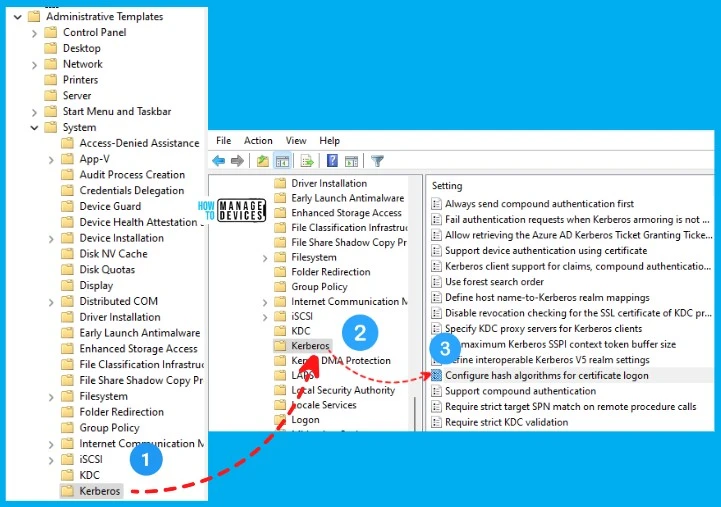
There are three (3) configuration options with Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon Authentication Group Policy. Those options are disable, configure, and enable. How do we decide which option? You can check the following table and get a granular option by selecting ENABLE option.
| SHA Algorithm = Default = Recommended State | More Granularity to Set each algorithm configuration |
|---|---|
| If the policy is set to DISABLE or Not Configure | If the policy is set to Enable |
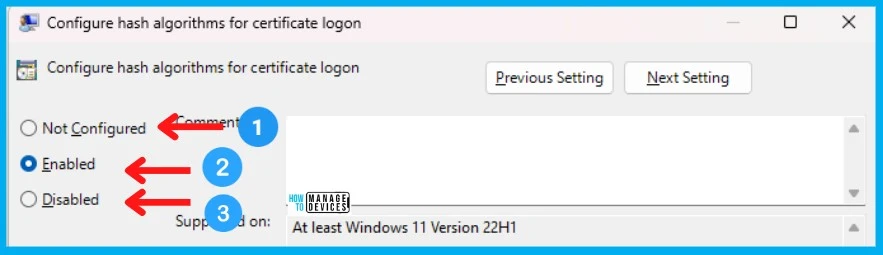
4 Supported States of Each SHA Algorithm
New Windows 11 Configure Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon Authentication Group Policy setting controls hash or checksum algorithms used by the Kerberos client. This performs the certificate authentication during Initial Authentication (PKINIT).
For each SHA algorithm, you would be able to configure one of the four (4) states explained below. The Audited state helps admins to migrate from one SHA algorithm to the next. The four states will be configurable only if the policy is ENABLED.
NOTE! – SHA-1 should be placed in the Not Supported state as per Microsoft recommendation. The “not supported” state is intended for algorithms that are deemed to be insecure.
| Default | Supported | Audited | Not Supported |
|---|---|---|---|
| This state sets the algorithm to the recommended state | This state enables the usage of the algorithm | This state enables usage of the algorithm and audit reports an event (ID 206) every time it is used | This state enables disables the usage of the algorithm |
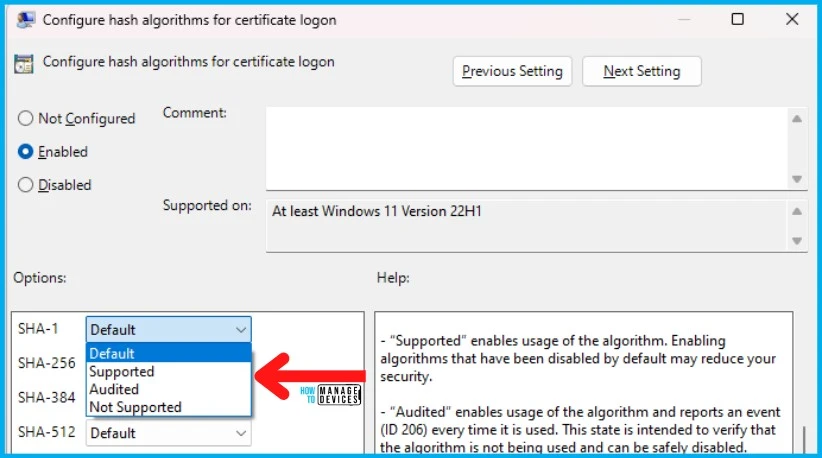
- “Default” sets the algorithm to the recommended state.
- “Supported” enables usage of the algorithm. Enabling algorithms that have been disabled by default may reduce your security.
- “Audited” enables usage of the algorithm and reports an event (ID 206) every time it is used. This state is intended to verify that the algorithm is not being used and can be safely disabled.
- “Not Supported” disables the usage of the algorithm.
New Windows 11 Event IDs
Let’s look at the new event IDs as part of Hash Algorithms for Certificate Logon Authentication group policy settings. There 4 new event IDs associated with this policy.
NOTE! – There is also a Windows MDM CSP associated with this policy, but there is no configuration available in Intune settings catalog for this policy.
Events generated by this configuration:
- 205
- 206 = SHA algorithm details are stored as event ID 206 for audit purposes.
- 207
- 208
Resource – 2019 SHA-2 Code Signing Support requirement for Windows and WSUS (microsoft.com)
Author
Anoop C Nair is Microsoft MVP! He is a Device Management Admin with more than 20 years of experience (calculation done in 2021) in IT. He is Blogger, Speaker, and Local User Group HTMD Community leader. His main focus is on Device Management technologies like SCCM 2012, Current Branch, and Intune. He writes about ConfigMgr, Windows 11, Windows 10, Azure AD, Microsoft Intune, Windows 365, AVD, etc.

