Data management is a multidisciplinary process that keeps data organized in a practical, usable manner. At its most fundamental level, the goal of data management is to ensure an organization’s entire body of data is accurate and consistent, readily accessible and properly secured.
Data management is a total life cycle information system that follows data from the moment it’s created until it ceases to be useful. As such, it involves tracking data from place to place, monitoring the transition of data from one form to another, and ensuring nothing important is left out of a business analytics model.
Data management also lays the groundwork for data analytics. Without a good master data management plan, analysis is practically impossible at worst and unreliable at best; we would be staring at an ocean of 1s and 0s with no way to make any sense of it all.
What is involved in a complete data management model?
While one might liken building a data management model to constructing a building, a better analogy would be a building that would grow beyond its foundation but still remain structurally stable and useful. The reason for this is that the goal of data management is to not just be able to structure and categorize data, but rather to be able to analyze it and make use of it in ways that were previously not imagined (Figure A). Proper data management grows with an organization.
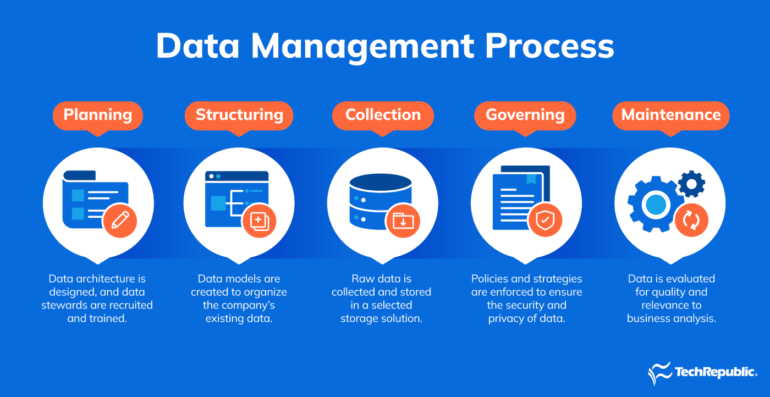
Planning
Planning covers the very thorough and comprehensive examination of how existing data is currently managed. For organizations that have never had a centralized data management strategy in place, the initial “structure” of that data might look more like a “junk drawer.” Yes, everything might be there, but finding it is difficult, and there may be more than one authoritative copy of what someone might be looking for.
SEE: Small businesses may want to consider these data management strategies.
For example, an organization may have inadvertently created two lists of employees, with the payroll department having one copy and the benefits department having another copy. Which one is correct? Which one should be used? Businesses must consider what they should do to maintain both lists.
Data structuring
Data structuring involves deciding how all of this unorganized data will be structured. Keep in mind that, even if data is structured and organized by one particular taxonomy, a proper data management solution won’t lock an organization to that taxonomy. The data will be able to be modeled in any manner that the organization sees fit. A properly-structured data management model will ensure that, for every kind of data, there is only one authoritative copy of it.
Going back to the example in the previous process, an ideal repository of employee information could be a single table, which contains all possible information about employees that any department within the organization could need.
Data acquisition and storage
Data acquisition covers the collection and importing of raw data from any number of different sources, along with converting or repackaging the data into a more structured format. From there, businesses must consider where data must be stored, be it in the cloud, on a server or someplace else, as well as what kind of storage solution is best for the purpose of the data.
Data safeguarding
An organization must not only implement and enforce data governance policies to govern which persons within the organization have access to the data, but it must also ensure data is protected against unauthorized access from anyone inside or outside of the organization. Data safeguarding must ensure data, like personal identifiable information, is further protected internally by the use of encryption and other security mechanisms.
SEE: The differences between data governance and data management.
Data maintenance
Data maintenance makes sure that, once data is properly managed, it does not revert to being the “junk drawer” that existed initially. This part of the model focuses on enforcing the structure that was created in the second process.
Data trailblazing
Data trailblazing takes an organization beyond the initial structuring created in the second process. This involves being able to use application or database programming to perform analyses of data that were not initially considered. This augments an existing data management model.
Benefits of data management
Properly-executed data management provides innumerable benefits to your organization. The single biggest benefit of properly managed data is not that you can query and analyze it in a flexible manner, but rather, you are not locked into a particular taxonomy that might restrict how that data could be analyzed.
Challenges of data management
Of course, proper data management is not without its challenges. Organizational inertia, resistance to change and having multiple disjointed data repositories that would need to be merged can create significant hurdles in creating a proper data management strategy.
Popular data management software
As with any major software platform, choosing the right data management tools from the onset can make a huge difference in an organization’s success. Data management can’t be done in a haphazard way — organizations will need to invest in data management solutions that can deliver all the results they need to be successful in managing and using data.
There are a number of data management tools, each with its own unique features and industries in which it fits. Some of the top platforms include:
- Collibra: Best for reference data management.
- Profisee: Best for managing large volumes of data.
- Hevo Data: Best for digital transformation.
- Google Cloud: Best for existing GCP users.
- Tableau Data Management: Best for unified data management and analytics.
When deciding on a platform, businesses should have a good understanding of the kind of data they have, how they want to host it and what their end goals for data management are. Armed with that information, a data management team can make the best choice possible for the needs of their organization.


