Let’s learn about the best set of updated Windows 11 Password Policies. We all know that Windows provides password protection to log in to PCs. Password policy makes users put in a password with some guidelines.
The IT industry is trying to get rid of passwords and looking forward to a Passwordless world in the near future. However, people use complex passwords to make their systems more secure, and no one can access them without permission. But some customization is also available to create the password using local group policy.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) gives added security. The users can customize password policies using the Local Security Policy and Elevated Command Prompt/Administrative Command Prompt to make changes as per requirements.
In this post, the step-by-step guidelines and the details are provided for better understanding. User and organizations can easily set their password complexity to protect their device from unauthenticated attackers.

- 4 Best Methods Enable Windows Sandbox | Configure Policies for Windows 11
- Microsoft Pluton Security Processor for Windows 11 and Enhancements
- Windows 11 Enhanced Password Phishing Protection
What are Windows 11 Password Policies
The password policy is a feature of windows 11 that decides the complexity of a password to login into windows. There are some requirements available to protect your device using a password. Password blocks unauthorized access.
Strong Passwords that are changed regularly reduce the chances of successful password attacks. The common method to authenticate a user’s identity is to use a secret password. A secure network environment needs all users to use strong passwords that at least fill up minimum requirements such as:
- Password minimum length at least eight characters
- Must include numbers (0-9)
- Include Uppercase letters (A-Z)
- Include Lowercase letters (a-z)
- Must include Symbols/special characters (!,@,#,$,%,<,^,&,* etc.)
Edit Windows 11 Password Policies Using Local/Domain Group Policy Settings
Open the Local Group Policy Editor and follow the path “Computer Configuration/Windows Settings/Account Policies/Password Policy” to reach the proper location to perform the desired task.
Note! – Let’s Open Run, type gpedit.msc, and press OK; the Local Group Policy Editor Opens. To open the Domain policy – Run gpmc.msc and press OK. More details domain level group policy settings using ADMX are explained -> Microsoft Edge ADMX Group Policy Templates.
Under the Password Policy, some options are there to customize the policy per the user’s or organization’s requirements. The options are presented below:
- Enforce Password History
- Maximum password age
- Minimum password age
- Minimum password length
- Minimum password length audit
- Password must meet complexity requirements
- Relax minimum password length limits
- Store passwords using reversible encryption
Computer Configuration/Windows Settings/Account Policies/Password Policy
Double-click each option to modify the default settings to the unique environment.
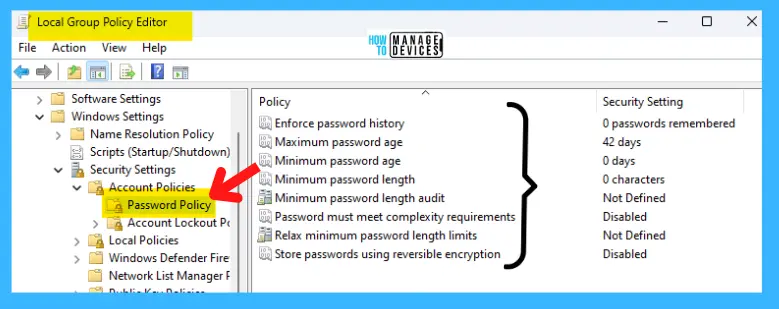
Enforce Password History for Windows 11
This security setting determines the number of unique new passwords that have to be associated with a user account before an old password can be reused. The value must be between 0 and 24 passwords. This policy enables administrators to enhance security by ensuring that old passwords are not reused continually.
- The default settings are 24 on domain controllers and 0 on stand-alone servers.
| Policy Name | Default Value |
|---|---|
| Enforce Password History – Domain Controllers | Do not keep password history – 24 passwords remembered |
| Enforce Password History – Individual Servers | Do not keep password history – 0 passwords remembered |
Note! By default, member computers follow the configuration of their domain controllers.
To maintain the effectiveness of the password history, do not allow passwords to be changed immediately after they were just changed by also enabling the Minimum password age security policy setting.
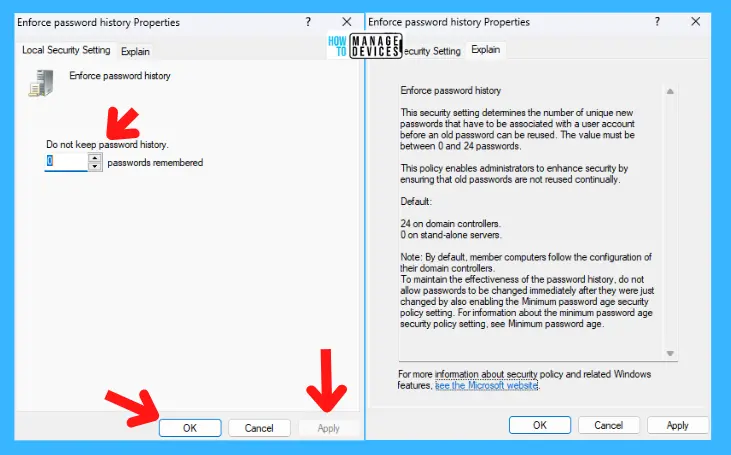
Maximum password age
This security setting determines the period of time (in days) that a password can be used before the system requires the user to change it. You can set passwords to expire after a number of days between 1 and 999, or you can specify that passwords never expire by setting the number of days to 0.
If the maximum password age is between 1 and 999 days, the Minimum password age must be less than the maximum password age. If the maximum password age is set to 0, the minimum password age can be any value between 0 and 998 days. The default age is set to 42 days.
Note! It is a security best practice to have passwords expire every 30 to 90 days, depending on your environment. This way, an attacker has a limited amount of time in which to crack a user’s password and have access to your network resources.
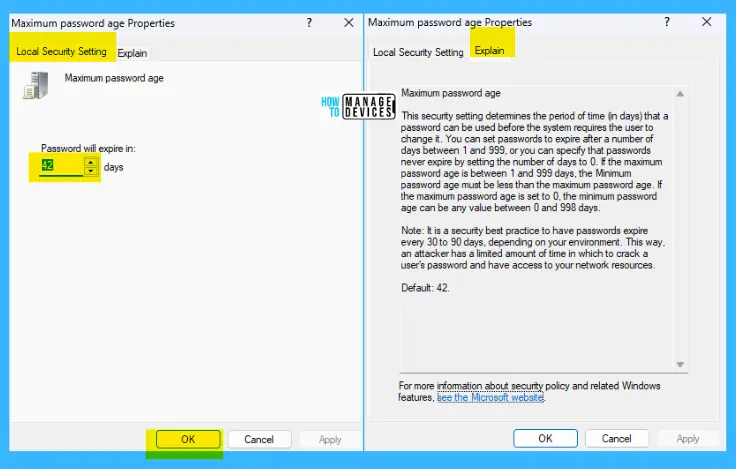
Minimum password age
This security setting determines the period of time (in days) that a password must be used before the user can change it. You can set a value between 1 and 998 days, or you can allow changes immediately by setting the number of days to 0.
The minimum password age must be less than the Maximum password age unless the maximum password age is set to 0, indicating that passwords will never expire. If the maximum password age is set to 0, the minimum password age can be set to any value between 0 and 998.
Configure the minimum password age to be more than 0 if you want Enforce password history to be effective. Users can cycle through passwords repeatedly without a minimum password age until they get to an old favorite.
The default setting does not follow this recommendation so that an administrator can specify a password for a user and then require the user to change the administrator-defined password when the user logs on. If the password history is set to 0, the user does not have to choose a new password. Enforce password history is set to 1 by default and 0 on stand-alone servers.
Note! By default, member computers follow the configuration of their domain controllers.
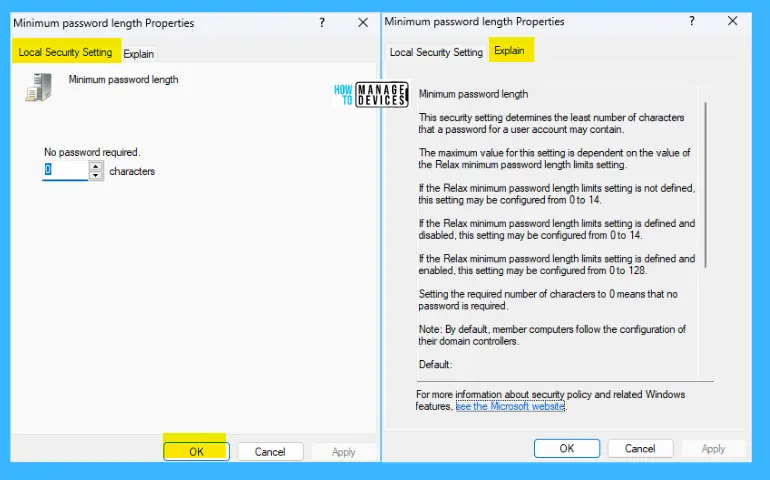
Minimum password length for Windows 11
This security setting determines the least number of characters that a password for a user account may contain. The maximum value for this setting depends on the value of the Relax minimum password length limits setting. If the Relax minimum password length limits setting is not defined, this setting may be configured from 0 to 14.
If the Relax minimum password length limits setting is defined and disabled, this setting may be configured from 0 to 14. If the Relax minimum password length limits setting is defined and enabled, this setting may be configured from 0 to 128. Setting the required number of characters to 0 means that no password is required.
Note! By default, member computers follow the configuration of their domain controllers.
The default value is 7 on domain controllers and 0 on stand-alone servers. Configuring this setting more than 14 may affect compatibility with clients, services, and applications. Microsoft recommends that you only configure this setting larger than 14 after using the Minimum password length audit setting to test for potential incompatibilities at the new setting.
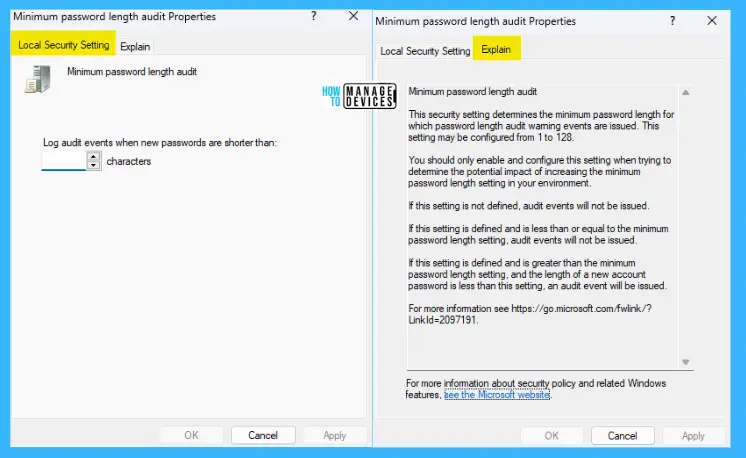
Minimum password length audit
This security setting determines the minimum password length for which password length audit warning events are issued. This setting may be configured from 1 to 128. You should only enable and configure this setting when determining the potential impact of increasing the minimum password length setting in your environment.
If this setting is not defined, audit events will not be issued. Audit events will not be issued if this setting is defined and is less than or equal to the minimum password length setting. An audit event will be issued if this setting is defined and is greater than the minimum password length setting, and the length of a new account password is less than this setting.
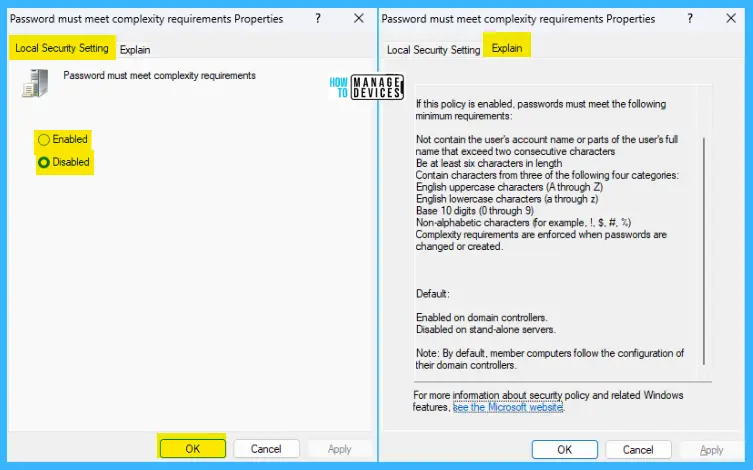
Password must meet complexity Requirements
This security setting determines whether passwords must meet complexity requirements. If this policy is enabled, passwords must meet the following minimum requirements:
- Not contain the user’s account name or parts of the user’s full name that exceed two consecutive characters
- Be at least six characters in length
- Contain characters from three of the following four categories:
- English uppercase characters (A through Z)
- English lowercase characters (a through z)
- Base 10 digits (0 through 9)
- Non-alphabetic characters (for example, !, $, #, %)
- Complexity requirements are enforced when passwords are changed or created.
The default setting is Enabled on domain controllers and Disabled on stand-alone servers.
Note! By default, member computers follow the configuration of their domain controllers.
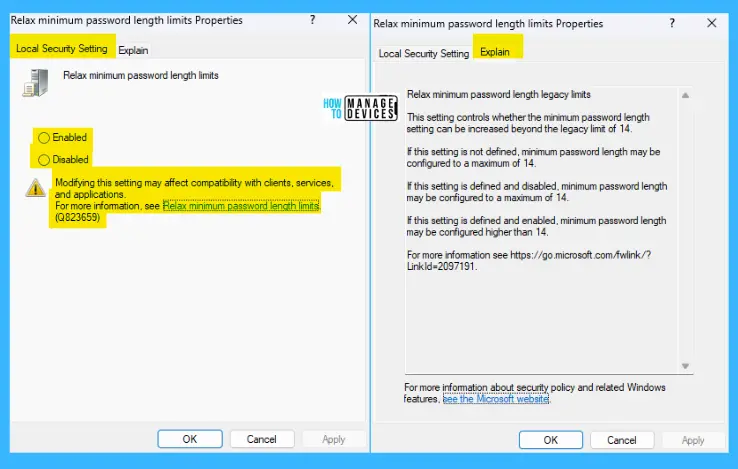
Relax minimum password length limits for Windows 11
This setting controls whether the minimum password length setting can be increased beyond the legacy limit of 14. If this setting is not defined, the minimum password length may be configured to a maximum of 14.
If this setting is defined and disabled, the minimum password length may be configured to a maximum of 14. If this setting is defined and enabled, the minimum password length may be configured higher than 14.
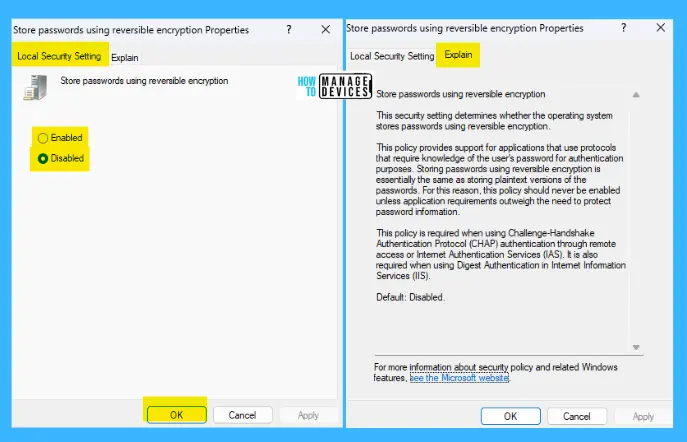
Store passwords using reversible encryption
This security setting determines whether the operating system stores passwords using reversible encryption. This policy supports applications that use protocols that require knowledge of the user’s password for authentication purposes.
Storing passwords using reversible encryption is essentially the same as storing plaintext versions of the passwords. For this reason, this policy should never be enabled unless application requirements outweigh the need to protect password information.
This policy is required when using Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) authentication through remote access or Internet Authentication Services (IAS). It is also needed when using Digest Authentication in Internet Information Services (IIS). The default setting is Disabled.
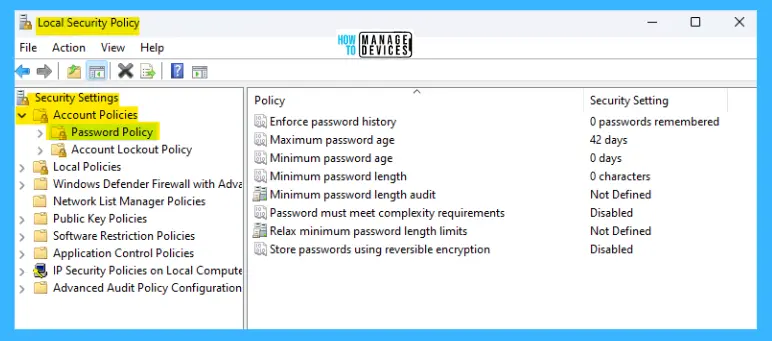
Edit Windows 11 Password Policies Using Local Security Policy Settings
To open the Local Security Policy, open the Run command and type secpol.msc, press OK. The Local Security Policy window opens, similar to the Local Group Policy settings; follow the procedures described above.
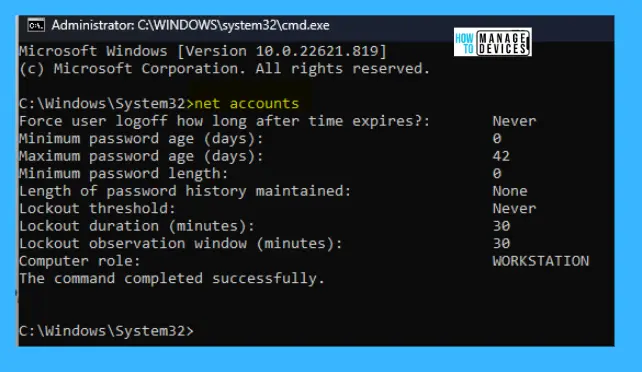
Windows 11 Password Policies Using Elevated Command Prompt
You can also customize the Password Policy by using the elevated command prompt. Open the Run command, type CMD, and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter. When the elevated command prompt/Administrative Command Prompt opens, type the command shown below and press ENTER:
- The below screenshot shows the list of options to customize the password policy.
net accounts
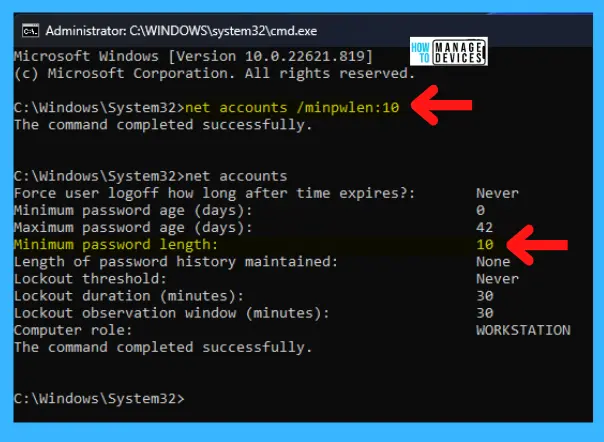
The above image shows the commands’ functionality, which helps you customize the password policy according to requirements. There are certain commands to execute the process, shown below:
- net accounts /minpwlen:value -> Replace the value with any number between 0 to 14, e.g., “minpwlen:6“
- net accounts /maxpwage:days -> Replace the days with any number between 1 to 999, e.g., “maxpwage:100“
- net accounts /minpwage:days -> Replace the days with any number between 1 to 999, e.g., “minpwage:2“
- net accounts /uniquepw:number -> Replace the number with any number between 0 to 24, e.g., “uniquepw:24“
Configure Windows 11 Password Policies Using Intune Policy Settings
You can configure Windows 10 or 11 password policy options with Intune or Group policy settings. Let’s look at Intune policy options to control Windows password policy. We have already seen how to customize password policy settings using Local Group Policy, Local Security Policy, and Elevated Command Prompt.
- Login to Intune Admin portal (EndPoint.Microsoft.com)
- Navigate to Devices – Configuration Profiles – + Create Profile
- Select Platform as Windows 10 and Later
- Select Profile as Templates
- Select Device Restrictions under templates
- Click on Create button
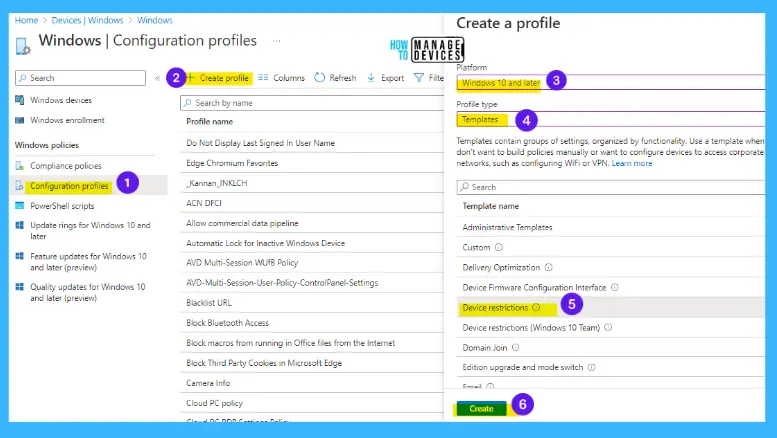
You can deploy Password Policies using Intune Device restriction policies.
- Enter the Name of the Intune Device Restrictions Profile
- Enter the Description HTMD Password policy using Intune out of box configuration profiles
- Click on the Next button
- Click on the Password Section from Configuration Settings
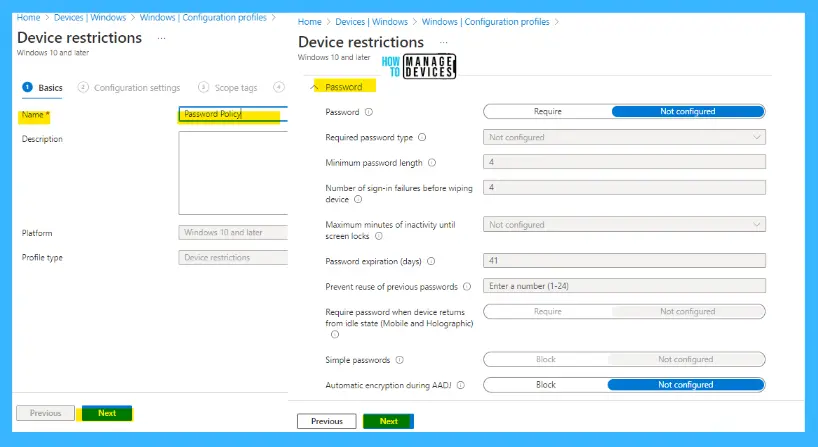
The detailed Intune Configuration process is described at Deploy Password Policies using Intune Configuration Profiles | Device Restriction.
I just wanted to let you know that customizing your windows password policy settings as described above is the process. Please follow us on Twitter HTMD Community and visit our website HTMD Forum if you like our content.
Author
Alok is a Master of Computer Applications (MCA) graduate. He loves writing on Windows 11 and related technologies. He likes to share his knowledge, quick tips, and tricks with Windows 11 or Windows 10 with the community.

